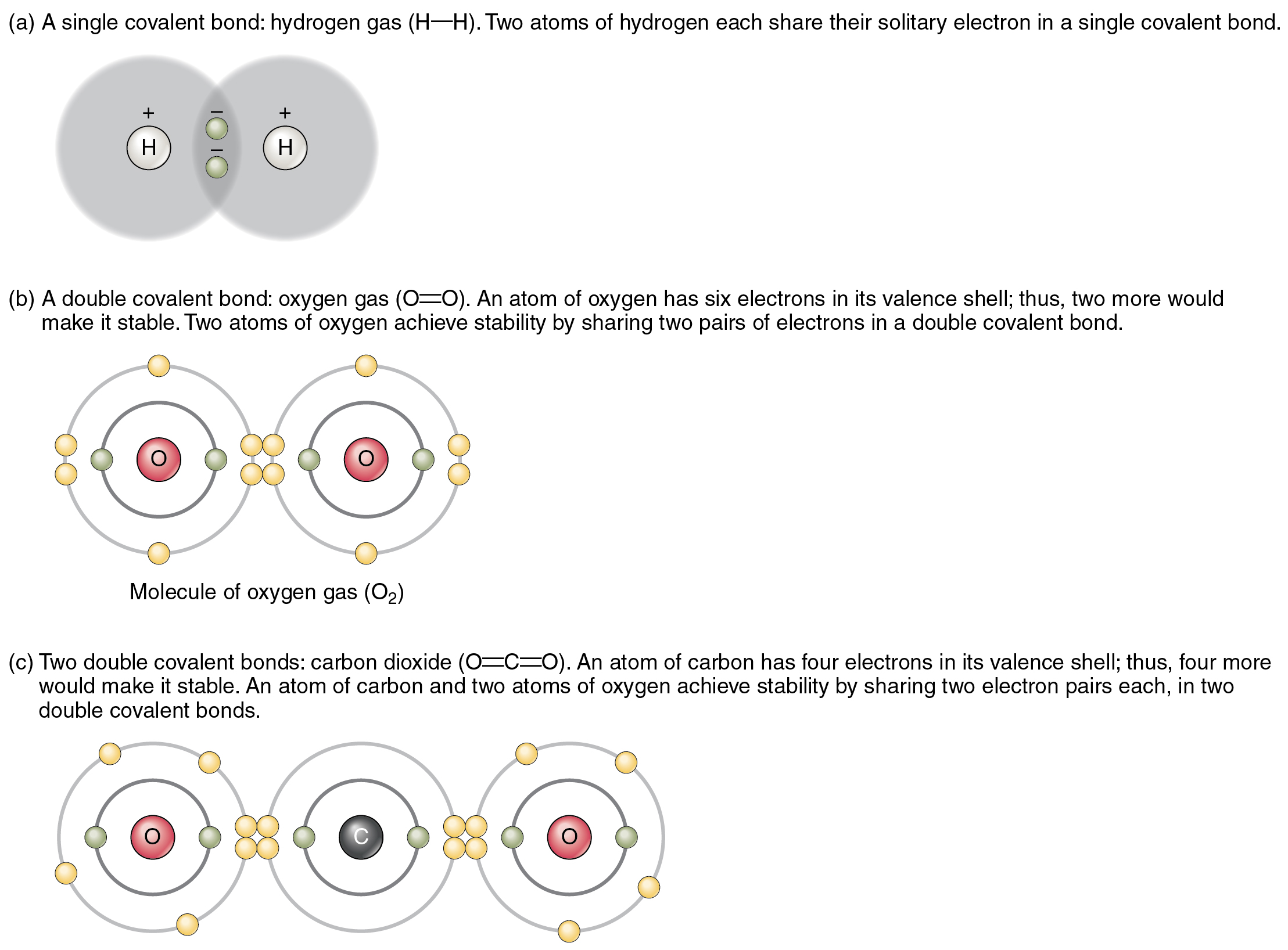
Does Hydrogen Form Ionic Bonds
Does Hydrogen Form Ionic Bonds - Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; Web ionic bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a. A hydrogen bond is weaker than an ionic. Web hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity. Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces. These oppositely charged ions attract. Hydrogen is tricky because it is at the. Web hydrogen bonds may form between atoms within a molecule or between two separate molecules. Web the hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding must be attached to electronegative atoms, such as o , n , or f .
Hydrogen bonds vs. Ionic bond YouTube
Web hydrogen bonds may form between atoms within a molecule or between two separate molecules. Web the hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding must be attached to electronegative atoms, such as o , n , or f . Web hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity. These.
Hydrogen Bond Definition, Types, and Examples
Web hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity. Hydrogen is tricky because it is at the. A hydrogen bond is weaker than an ionic. Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces. Web ionic bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a.
PPT The attraction between a hydrogen atom on one water molecule and the oxygen atom on
Web ionic bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a. These oppositely charged ions attract. Web the hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding must be attached to electronegative atoms, such as o , n , or f . Web hydrogen bonds may form between atoms within a molecule or between two.
Hydrogen Atom Hydrogen Atom Form An Ionic Bond
Web hydrogen bonds may form between atoms within a molecule or between two separate molecules. Hydrogen is tricky because it is at the. These oppositely charged ions attract. Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; A hydrogen bond is weaker than an ionic.
[DIAGRAM] Labeled Diagram Of Hydrogen Bonding
A hydrogen bond is weaker than an ionic. Hydrogen is tricky because it is at the. Web hydrogen bonds may form between atoms within a molecule or between two separate molecules. These oppositely charged ions attract. Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces.
Ionic Bonding Presentation Chemistry
A hydrogen bond is weaker than an ionic. These oppositely charged ions attract. Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; Web ionic bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a. Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces.
Chemical Bonds Ionic, Covalent, and Hydrogen YouTube
These oppositely charged ions attract. Web hydrogen bonds may form between atoms within a molecule or between two separate molecules. Web hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity. Web the hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding must be attached to electronegative atoms, such as o , n .
Chemical Bonds · Anatomy and Physiology
These oppositely charged ions attract. Web the hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding must be attached to electronegative atoms, such as o , n , or f . A hydrogen bond is weaker than an ionic. Web hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity. Covalent and ionic.
Image and Video Gallery National Institute of General Medical Sciences
Web the hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding must be attached to electronegative atoms, such as o , n , or f . Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces. A hydrogen bond is weaker than an ionic. Web ionic bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a. Web hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen Atom You Are The Most Important Electron In A Hydrogen Atom
Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; Web hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity. These oppositely charged ions attract. Web the hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding must be attached to electronegative atoms, such as o , n , or f . Web hydrogen bonds may form between.
Web hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity. Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces. Hydrogen is tricky because it is at the. A hydrogen bond is weaker than an ionic. These oppositely charged ions attract. Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; Web ionic bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a. Web the hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding must be attached to electronegative atoms, such as o , n , or f . Web hydrogen bonds may form between atoms within a molecule or between two separate molecules.
Web Hydrogen Bonding, Interaction Involving A Hydrogen Atom Located Between A Pair Of Other Atoms Having A High Affinity.
Hydrogen is tricky because it is at the. Web hydrogen bonds may form between atoms within a molecule or between two separate molecules. Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces. Web the hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding must be attached to electronegative atoms, such as o , n , or f .
These Oppositely Charged Ions Attract.
Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; Web ionic bond, type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a. A hydrogen bond is weaker than an ionic.


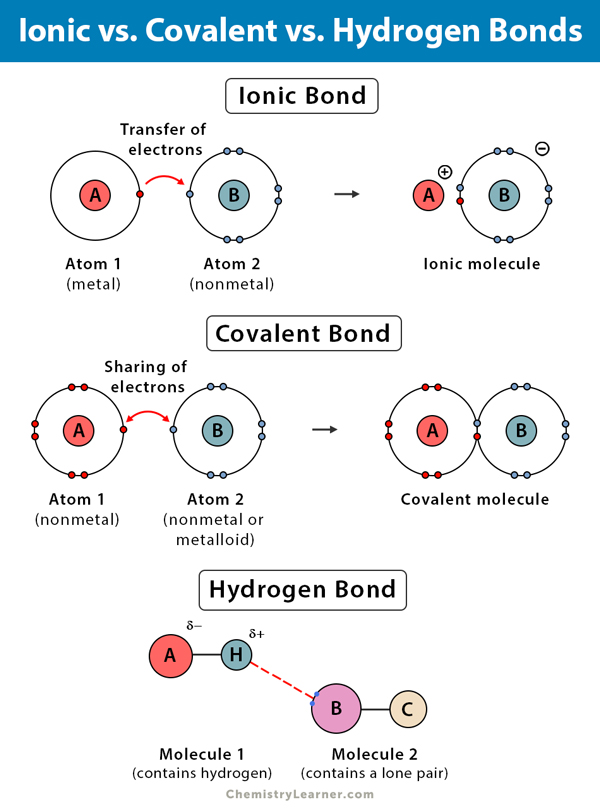


![[DIAGRAM] Labeled Diagram Of Hydrogen Bonding](https://i2.wp.com/ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu/webproj/211_fall_2016/Roger_Vang/Roger_Vang/Hydrogen Bonding.png)
.PNG)