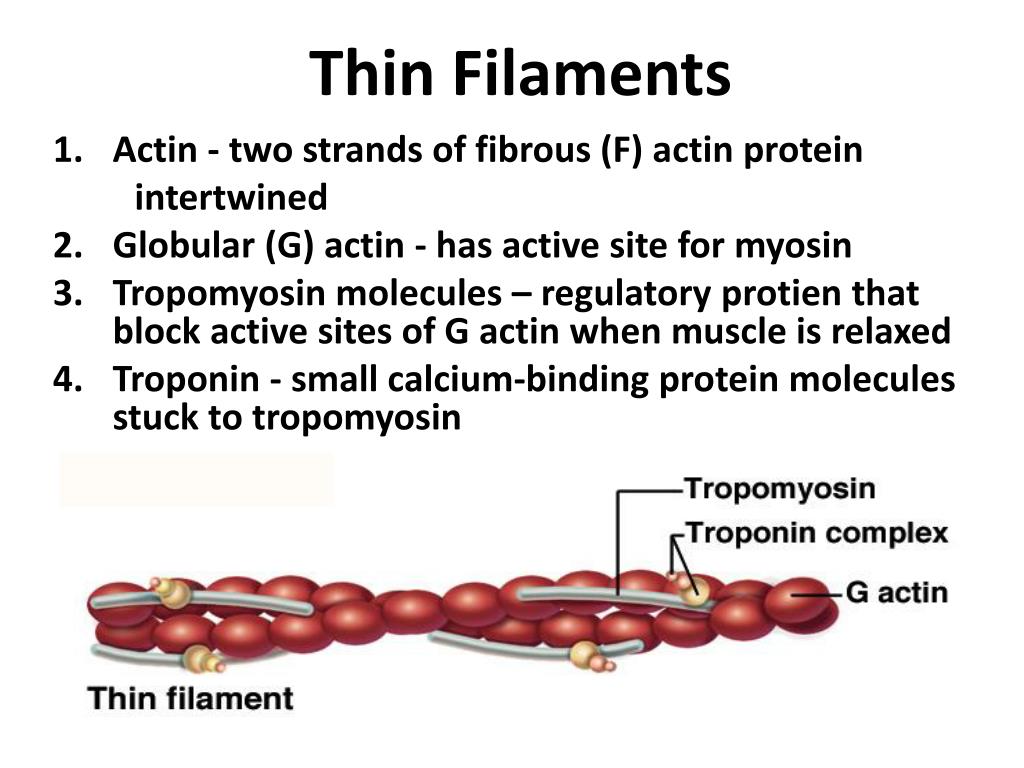
This Contractile Protein Forms The Thin Filaments
This Contractile Protein Forms The Thin Filaments - Molecule consists of a tail and two myosin heads, which bind to myosin. Web actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament) interact to form the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. Web an individual sarcomere contains many parallel actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments. Web the contractile protein that forms the thin filaments. Web the sarcomere is the main contractile unit of muscle fiber in the skeletal muscle. The interaction of myosin and. Each actin microfilament is a polymer known as f. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the actual contractile units of muscles extend from z disc to z.
Skeletal Muscle Structure and Contraction BIO103 Human Biology
Web the sarcomere is the main contractile unit of muscle fiber in the skeletal muscle. Each actin microfilament is a polymer known as f. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the actual contractile units of muscles extend from z disc to z. Web the contractile protein that forms.
Sliding Filament Model of Contraction Biology for Majors II
The interaction of myosin and. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the actual contractile units of muscles extend from z disc to z. Each actin microfilament is a polymer known as f. Web an individual sarcomere contains many parallel actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments.
MUSCULAR TISSUE CONTRACTILE STRUCTURES CELLS AND FIBERS
Web the contractile protein that forms the thin filaments. The interaction of myosin and. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Web an individual sarcomere contains many parallel actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments. Web the sarcomere is the main contractile unit of muscle fiber in the skeletal muscle.
Structure of contractile proteins YouTube
The interaction of myosin and. Each actin microfilament is a polymer known as f. Web actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament) interact to form the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Web an individual sarcomere contains many parallel actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments.
Muscle Tissue Basicmedical Key
Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the actual contractile units of muscles extend from z disc to z. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Web the sarcomere is the main contractile unit of muscle fiber in the skeletal muscle. The interaction of myosin and. Web the contractile protein that forms the thin filaments.
This contractile protein forms the thin
Web actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament) interact to form the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. The interaction of myosin and. Web an individual sarcomere contains many parallel actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments. Molecule consists of a tail and two myosin heads, which bind to myosin. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament;
Thin Anatomy
Web actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament) interact to form the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. The interaction of myosin and. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Molecule consists of a tail and two myosin heads, which bind to myosin. Web the sarcomere is the main contractile unit of muscle fiber in the skeletal muscle.
Structure of Contractile Proteins YouTube
The interaction of myosin and. Each actin microfilament is a polymer known as f. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Web actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament) interact to form the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. Web an individual sarcomere contains many parallel actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments.
IJMS Free FullText Thick and Thin Filament Gene Mutations in Striated Muscle Diseases
Molecule consists of a tail and two myosin heads, which bind to myosin. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Each actin microfilament is a polymer known as f. The interaction of myosin and. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the actual contractile units of muscles extend from z disc to z.
Thick and thin filaments. Human anatomy and physiology, Physiology, Anatomy and physiology
Molecule consists of a tail and two myosin heads, which bind to myosin. Web actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament) interact to form the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the actual contractile units of muscles extend from z disc to z. The interaction of myosin and. Web the.
Each actin microfilament is a polymer known as f. Web an individual sarcomere contains many parallel actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments. Molecule consists of a tail and two myosin heads, which bind to myosin. Web the contractile protein that forms the thin filaments. Web actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament) interact to form the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. The interaction of myosin and. Web the sarcomere is the main contractile unit of muscle fiber in the skeletal muscle. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the actual contractile units of muscles extend from z disc to z.
Web The Contractile Protein That Forms The Thin Filaments.
Web the sarcomere is the main contractile unit of muscle fiber in the skeletal muscle. Web actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament) interact to form the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. Web contractile protein that makes up thick filament; Molecule consists of a tail and two myosin heads, which bind to myosin.
Each Actin Microfilament Is A Polymer Known As F.
The interaction of myosin and. Web an individual sarcomere contains many parallel actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the actual contractile units of muscles extend from z disc to z.